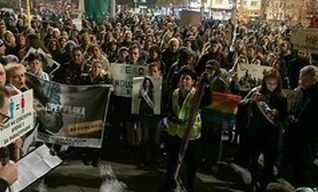Under Assault: Class and Gender in Bulgaria and Europe Today
Bulgarian Left Feminists LevFem: “We are in the midst of a class assault. It is impossible to think of it outside of gender.”
Photo: Names of victims of gender-based violence written down by protesters, 26/11/2019 Sofia, photo credit: Neda Genova.
The following interview was conducted by Hannah Schultes with three of the members of LevFem
– a newly formed anti-capitalist queer-feminist collective in Sofia,
Bulgaria. LevFem participated actively in the mobilization of the
protest that marked the International Day Against Violence Against Women in
Sofia in 2018. The collective emerged a few weeks prior to the protest
to place socio-economic inequalities as part of the feminist agenda in
Bulgaria. It has also urgently called for mobilizing against the rising
tide of racism, neofascism, ethnophobia, and xenophobia in Bulgaria and
the region. The interview was conducted in December, 2018.
Interviewed: Zhivka Valiavicharska, Neda Genova, Raia Apostolova
Hannah Schultes: On the 27th of July, 2018 the Constitutional Court ruled that the Istanbul Convention is incompatible with the Bulgarian constitution. Even the Bulgarian Socialist Party positioned itself against ratifying the Istanbul Convention at the beginning of the year. Why was there such an unanimous position against the Convention?
LevFem: The debate around the ratification of the Istanbul Convention can be described as symptomatic of the political climate in the country in that it made use of a conservative, right-wing rhetoric where the social and political concerns behind the Convention’s text itself were of little importance for those who managed to dictate the terms of the debate to such an extent that they could actually block its ratification. The quest to ward off ‘foreign influence’ and ‘gender ideology’ united politicians and so-called opinion makers across the political spectrum: from far-right coalitions such as the United Patriots to allegedly socialist parties like the Bulgarian Socialist Party (BSP), to, finally, the ruling party, GERB. BSP’s decision to take an official position against the Convention’s ratification can only be shocking to someone who is not acquainted with the Bulgarian political landscape and the fact that despite being nominally on different sides of the political spectrum, party members usually share an interest in maintaining the status quo, especially by catering to (and fueling) nationalist tendencies, supporting the interests of business, and so forth. While the electoral support for far-right parties is around 10% and has actually dropped slightly in the past 10-15 years, its rise to prominence has, as in many other countries, made centrist and ‘left’ political parties lean further to the right. The simple answer to the question is thus that the position against the Convention was so unanimous because the ruling powers (GERB, the United Patriots, BSP) are also unanimously more concerned to maintain the status quo (that is, their control of public institutions on all levels of government and society) at the expense of a politics driven by concern for the improvement of the conditions of the disadvantaged, dispossessed, excluded, marginalised people, or even for the wellbeing of the majority. The easiest (and most effective) way for politicians to maintain this status quo is to divert popular discontent from themselves to some vaguely defined, sometimes even nonexistent, threatening enemy – such as the obscure ‘gender ideology’ which became an object of so much tremor this year. But at the same time, the queer and feminists movements are a very real threat to the patriarchal order and the often violent forms of gender-based, ethnic, nationalist, and racial supremacies it rests on.
What was so scandalous about adopting the Istanbul convention?
At the heart of the ‘scandal’ stood an at first seemingly insignificant misunderstanding of the term ‘gender’ which was used in the expression ‘gender-based violence’ in the text of the Istanbul Convention. ‘Gender’ has no direct translation in the Bulgarian language and is thus commonly transliterated, making it sound foreign and unfamiliar to many people, who vaguely associate it with gender-queer people and LGBTQ politics. The conservative politicians and spokespersons who took up the crusade against the Convention produced and mobilised a social imagery of a ‘foreign threat’ of a ‘gender invasion’, where things such as the destruction of the ‘traditional Bulgarian family’ and the ‘introduction of a third gender’ were earnestly discussed as menaces to the country’s sovereignty. They implied that there is some kind of conspiracy against Bulgarian society led by foreign powers who aim to subvert its founding pillars. We could thus see how queer, gay and lesbian, and gender-nonconforming people (whose rights and safety were actually never the primary concern of the Istanbul Convention) were turned into scapegoats and instrumentalised for the uses of conservatives who needed to create an ‘enemy’ against whom to mobilise popular discontent and fear. All this was formulated mostly within nationalist frameworks, and it mobilized extreme nationalist formations and sentiments: people who showed up for the anti-Istanbul Convention protests to stand for ‘traditional family values’ (read, the patriarchal subordination of women and their confinement to heterosexuality and reproductive labor) see women’s autonomy, as well as queer and gender-nonconforming people and practices, as a threat to the Bulgarian nation in the same way that they see migrants and refugees as a threat to national integrity and the ‘survival’ of the nation, and regularly fuel racist and ethnophobic politics towards the country’s ethnic and religious minorities.
The International Day Against Violence Against Women was observed in Sofia on November 26th. There were solidarity protests in Berlin, London, Bucharest and Prague in front of the Bulgarian embassies, and in Canterbury. But solidarity from feminists in Western European countries like Germany might easily be seen as liberal elitism in Bulgaria. Why should feminists in Germany nevertheless show solidarity?
We appreciate this question – for us the question about solidarity is more about ‘how,’ and from what position feminists in Germany show and build solidarity with feminist movements and mobilizations in Bulgaria, other Balkan and East-European countries, and other parts of the world. We are aware that feminism in Germany is not a homogeneous or self-contained movement, and that feminists in Germany are not a unified collective subject with a singular history. We remain attentive to the particular social, political, and historical contexts that women and queer people in Germany face as they experience and confront multiple social differences, including class inequalities, racial, ethnic, and religious differences, migrant histories and backgrounds, and the movements’ historical and contemporary entanglements with other locations and continents, including Bulgaria and the Balkans. These moments often form the fractured and painful fabric of the movements, but they contain tremendous productive energy and important lessons and connections. It is with these political sensibilities and commitments in mind that we appreciate immensely the support and solidarity of feminists in Germany and are hoping to build and strengthen our bridges. Here at LevFem we do not conflate this solidarity for the kind of ‘universal sisterhood’ that women in Western Europe and North America constructed in the 1980s in problematic ways – not only in the liberal currents of the movements but also on the left – that presumed Eurocentric, Western, and developmentalist norms as their points of departure. We have much to give and learn from each other and share with each other in moments of intense mobilization, and also in every other moment, while confronting social realities with awareness of our particular contexts and histories.
What are the particular reasons that LevFem called for solidarity actions at the end of November 2018?
Because there is a reactionary patriarchal and right-wing movement that resonates with other trends in the region, Europe, and the world, and concerns all of us globally, and because we believe feminism is an issue that calls for solidarity across different locations and contexts, including national, regional, and transcontinental. We think that the feminization of many labor sectors and the assault that comes from above aiming at the destruction of our access to the means of social reproduction is an organized attempt that solidifies violence against women and intensifies their subordination, forcing women into dependence and social marginalization. Both exploited at their workplaces and placed in the position to care for future and present laborers, it forcefully reinscribes the so-called double burden.
What is the situation of women in the Bulgarian labor market?
The past thirty years in Bulgaria are a striking example of this assault from above. Countries in Eastern Europe have become the ground for some of the most radical neoliberal economic reforms and experiments.
Recent research made by the Clean Clothes Campaign shows that
international companies such as H&M use Bulgaria, among other
countries, as a pool of cheap labor. The labor force in these factories
is predominantly women who are forced to work in unbearable conditions,
which is the result of thirty years of labor deregulation. Of course,
H&M is not the only company to do this. Eastern Europe has been
produced as a region where the extraction of cheap labor prevails as a
form of commodification and international lobbies make sure this stays
intact as we saw in the recent developments regarding the transport workers.
Yet women suffer disproportionately because they are framed as the ones
responsible for reproductive care and domestic work, and this produced
condition is accompanied by the diminishing of state-sponsored
kindergartens, schools, kitchens and other public institutions that
aimed to at least alleviate the double burden and reconfigure
reproductive care as a societal responsibility during socialism. This
kind of precarity dramatically increases the risk of women falling
dependent on men and disproportionately exposes them to domestic and
sexual violence. It is precisely in this context that we should see the
disturbing increase in the number of women murdered by their domestic
partners, and generally the intensification of patriarchal relations in
Bulgaria, along with the rise of right-wing nationalism.
In the past years, many Bulgarians have migrated to Germany in order to improve their situation. What is the role of Western European countries in this picture of a neoliberal assault on the Bulgarian workforce?
This
kind of precarity is an issue that goes beyond national or local
contexts because it is pushed by international business lobbies such as
BusinessEurope, and it shows that immigrants, refugees, people of color,
and marginalized working class populations are often the direct target
of this intensifying class subjugation. A law recently passed in
Austria, for example, reduced child benefits for foreign workers and
forced them to rely on the benefits provided by their home countries.
Germany was also involved in these efforts to geographically decouple
social security and labor processes. These laws are openly
anti-immigrant, following a classic xenophobic logic that extracts cheap
labor from migrant workers while systematically excluding them from
public benefits and assistance programs, even when they equally
contribute to these systems. As we know, this is affecting migrant and
mobile working populations coming mostly from countries such as Bulgaria
and Romania, and the problem is exacerbated by the fact that childcare and other public assistance programs in these countries are absurdly low. In
other words, this kind of neoliberal assault has intensified class
inequalities and subjugation, further marginalizing women, migrant
people, and people of color, and rendering entire regions abject and
thereby exploitable, and it is being waged precisely on the terrain of
social reproduction. In this sense what has been happening in
postsocialist Bulgaria and other postsocialist countries in the past
thirty years provides a context that illuminates in particular ways,
perhaps dramatically, larger trends that affect many others, and it
resonates with similar developments and experiences in different parts
of the world.
A recent example for what you describe from the Bulgarian context is the Bulgarian Industrial Capital Association that wants to lower the period and amount of pay for maternity leave in the country. What are their arguments and how is this demand discussed in the public?
The
Bulgarian Industrial Capital Association was empowered by a decision of
the European Court that argued, essentially, that parental leave is not
work and hence it cannot be counted towards the accumulation of
vacation days of a parent who has returned to work. This was the point
when BICA, and other local business lobbies, started to make serious
noise regarding the two-year ‘maternity’ or parental leave in Bulgaria.
(Legally, these are ‘maternity’ benefits, which the mother can transfer
to the legal father or to a grandparent six months after birth or
adoption – although they are most commonly claimed by the mother.) At
first, the business lobbies called for a reduction in the right to two
years of parental leave. This noise eventually stopped as many workers
expressed complete disapproval of such proposals. Then, BICA tried to
argue that at least the amount of money paid during the first year of
the parental leave should be lowered (currently it is calculated at the
rate of 90% of the average daily gross remuneration taken for the past
24 months). Before 1989, these benefits translated into substantial
support. But in the last thirty years, with the massive devaluation of
labor, 90% is in fact very little for the majority of the working
population. Many women are unemployed, or work sporadically, or
illegally, which affects the amount of social aid they receive. This is
further complicated by the fact that many, if not the majority of
employers, pay social security at the minimum wage even if they pay
higher wages to their workers, which hits families in the amount of
money they receive as ‘maternity’ leave. The amount women and parents
receive in the second year is even more insignificant. It amounts to
only 160 EUR (380 BGN) per month. Today, for the most part, media
discussions of the Association focus on its demand that, following the
European Court’s decision, ‘maternity’ leave does not count as work,
which will rob child-caring family members, the vast majority women, of
vacation days after they return to work and perhaps even more benefits,
as is still to be seen.
What will be the consequences if capital associations are successful in these attempts?
Essentially,
we are in the midst of a class assault, the outcome of which is still
unknown, but what is happening makes it impossible to think of it
outside of gender, race and ethnicity, because women, and especially
those from the Bulgarian Roma ethnic minority, are at the forefront of
the attack on resources for reproductive and care work. If the
propositions from above are achieved, this will be detrimental to the
workforce in the country and we will witness a Catch 22 situation.
Lowering the amount of paid leave or getting rid of the second year
means that social reproduction will be so endangered that the recipients
of these benefits will be forced to go back to work shortly after birth
or adoption, and will follow a model that we see in the United States
for example. This is on the one hand. On the other, thе rapid return to
work is in fact extremely difficult because there are not enough
affordable kindergartens, schools, afterschool programs, etc., due to
high levels of privatization in the public sector. Some
liberal voices claim that shortening the parental leave is a good idea
because otherwise the caregivers lose ‘labor habits’, staying at home
bores them, they stop developing entrepreneurial skills, etc. In fact,
BICA has adopted the same arguments. These voices often see the
necessity of more childcare facilities but do not really care if they
are privately owned, and we know that privatization negatively hits the
poor – which is the majority of people in Bulgaria. We see clearly how
class and gender intersect here. Since there is very limited access to
socialized means of social reproduction in the public sphere, if we do
not pay very careful attention to these arguments, we risk eventually
seeing a full displacement of care from the public to the private
sphere. Such claims, which frame caregivers and women solely according
to their ‘labor habits’, reduce them to purely economic subjects. In
this doctrine, the interests of the market are postulated as most
central and primary; they come to dominate all social spheres and modes
of subjectivation. We disagree with this argument precisely because we
try always to think through the double burden and because we do not
believe that our freedom depends on participating in a labor process
that enriches somebody’s private interest.
Mainstream media portrays the comparatively long maternity
leave along the lines of Bulgaria ‘being the ideal place’ for ‘starting a
family’. An article I came across has the title ‘Why US mums are
envious of Bulgarian ones’. So if Western media outlets notice, that in
that regard ‘many of the top ranking policies are in Eastern Europe’,
what is lost in that picture?
These
social gains were the legacy of the last three decades of socialism,
thanks to the intense mobilization and organizing of activists in the
movement. As our comrade and LevFem member Zhivka Valiavicharska
explores in her work, feminist movements in the socialist countries from
the 1970s made social reproduction a central focus of their work in a
way that extends way beyond its uses in Marxist and left-feminist
traditions in the West. She shows that the socialist meanings of social
reproduction included more familiar notions such as biological
reproduction, domestic and care work, housing, food, and healthcare, as
well as some institutions such as the school and the ‘family.’ Yet they
also included leisure, rest, culture, creative activity, social life,
and generally a range of social activities that in some ways displaced
the dominant role of ‘labor’ as an organizing social principle, or
rather saw it as one aspect of a more expansive picture of social and
creative life. These
struggles managed to make social reproduction central to the meaning of
socialism – in other words, they pressed the question, what kind of
society is this if it doesn’t take collective responsibility for
social-reproductive needs and activities, if it doesn’t make them a
shared social responsibility at large? This way activists in the
movement eventually made the government allocate resources for and build
vast infrastructures of care, leisure, culture, and creative activity.
These infrastructures socialized social-reproductive and care work in
unprecedented ways. The child benefits and the two-year parental leave
are a legacy of this work, together with what used to be a vast network
of public daycare centers, kindergartens, afterschool programs,
cafeterias, student housing, creative and recreational facilities. These
material conditions opened possibilities for women to have more social
autonomy and mobility, and had the potential to break down gendered
divisions of labor, generally reaching deep into the material structures
of class and patriarchal subjugation to break them down. Statistics
show that some of these reforms accomplished remarkable results and yet
some remained what we call ‘socialist potentials’. Here we define
‘potential’ in direct opposition to the bourgeois economist notion of
potential, which thinks of the individual solely as a resource and a
potential source of profit. The socialist potential is a potential which
lays the foundation of socializations of the means of social
reproduction, of mobility and equality, among others.
What were the limitations of these feminists’ socialist politics?
The designs of these socializations carry the mark of their times and had uneven effects. For example, in line with a good deal of feminist work of the 1970s in the West but also in other places, they adopted binary and heterosexual notions of gender and sexuality and essentialized women’s bodies. They privileged the biological mother as the primary caregiver, turning ‘motherhood’ both into a dictate of nature and a social duty. Because of these and other patriarchal notions still intact, this kind of labor remained largely feminized, even if it was more socialized. It is also not surprising that these policies became entangled in the most disturbing ways in population-management projects and ethnonationalist visions of nationhood. History has shown that women’s bodies and social lives have often become the terrains of these biopolitical projects in the most intense ways. In the early 1970s, there was a pro-nativist turn in countries such as Bulgaria and Romania, which restricted or completely banned abortions, respectively, while enhancing maternity and childcare benefits. Up until then, abortions in Bulgaria had been legal and freely accessible since 1957. The restrictions on abortion introduced in Bulgaria in the early 1970s were abolished in 1991, but their parameters show the kinds of normative models of family, sexuality, and affective relationships that were pushed through these reforms, often violently so. There is a law passed in 1985, which practically turns ‘maternity’ benefits into ‘parental’ or even partial ‘kinship’ benefits, granting access not only to the legal father but also to a grandparent who can claim primary responsibility for the care of a child – but only six months after birth or adoption. This is an ambivalent formulation as it still posits the mother as the primary parent and confers upon her the primary responsibility of care, at least for the first six months. At the same time, it is extremely interesting not only because it recognizes the responsibility of the ‘father,’ but also because it is a material and social recognition, if limited, of the kinds of kinship and community care networks involved in raising children and the multiple forms of parenthood practiced ‘on the ground’ that defy modern Western models of the nuclear family. We believe this is still in place. It is unclear to what extent it had any tangible effects in changing patriarchal perceptions that see parenthood and childcare as women’s ‘obligation’. However, they at least opened the material and legal conditions in some intriguing directions.
How does LevFem relate to this legacy?
This is a very general sketch which outlines some of the socially-beneficial as well as the disturbing aspects of this legacy. We have to emphasize its social and historical value, and fight to preserve it especially now, when it is being rapidly dismantled. We also believe we have the hindsight and some different tools to assess it critically and we have to fight to change the problematic elements embedded in it. Some of this work includes demanding the denaturalization of motherhood and parenthood; breaking down the heterosexual and gender-binary models it is built on; fighting for equal access for queer people, for universal access to assisted reproduction; emphasizing alternative and communal forms of parenthood, which actually have a strong presence and history in the local social cultures; and importantly, relentlessly fighting patriarchal culture and violence in all its forms. The assault on social-reproductive resources from the last two-three decades has been happening in an intense anti-left and anticommunist climate, which has enabled the political alliance between neoliberal, right-wing liberal, nationalist, and neofascist formations, currently holding power on many levels. This is all coming in addition to the absurdly low amounts of the actual benefits, calculated on the basis of an impossibly low minimum wage.
At the end of 2018, Bulgaria saw a wave of protests against higher fuel prices, tax increases for older cars and an expected increase in car insurance premiums. Who were the protesters and how did the protest develop?
Yes,
November was marked by a wave of protests, which, like the ‘yellow
vests’ in France and the protests in Belgium, rose against the hike in
the fuel prices and car insurance premiums. The rebellions were
comprised of precarious workers, self-employed, men and women,
unemployed and workers from various sectors with varying degrees of
security. The protests were more numerous and organized in cities
outside of Sofia. November 11th, for example, was marked by
demonstrations, street barricades and ‘snail chain’ actions in more than
thirty Bulgarian cities. Although protesters were at first voicing
their anger against the hikes, which would raise considerably their
costs and expenses, soon enough it became evident that their objectives
were much larger and systemic. ‘System change!’ and ‘Resignation!’ were
chants that thundered through. Despite the wide social class composition
of the protesters, one thing was clear: the protests were class
protests.
In what way?
Sofia-based journalist and sociologist Chavdar Naidenov perhaps best explained what was taking place in the country. His article (in Bulgarian) for the local left-wing magazine Barikada, opened
with the following question: “People are protesting against high fuel
prices. In 1997 they were blocking the railroads, now they are blocking
the highways. Can you sense the difference?” With
the notion of the fuel-dependent worker, Naidenov described the
policies of Borisov’s cabinet, which was for years busy motorizing the
country with low-quality roads and highways, built with cheap materials
and numerous defects, while destroying public transport infrastructures.
The fuel-dependent worker is one whose dependency is an effect of years
of brutal privatization of the commons and the public infrastructure,
which did not spare the transport sector. And even when separate
elements of this sector are still state-owned, the state is in fact so
passive in maintaining them that the whole operation reminds us of the
ruthless practices during the liquidation of state enterprises in the
early 1990s, when machinery was stolen in broad daylight before the very
eyes of the workers. In fact it has been a common tactic of those in
power from the last thirty years to deliberately defund and leave in
neglect the public infrastructures so that they can be bankrupted and
sold out for nothing. One such instance is the Bulgarian State Railways,
which has been chronically defunded and driven into insurmountable
debt, and it has lost most of its constant capital. It is still the most
affordable means of transportation, but it is currently falling apart
and dangerous to use because most of its active trains haven’t been
repaired, purposely, since the last decade of socialism, and accidents
are common. So the fuel-dependent worker is the effect of this
destruction of the public infrastructure and the result of years of
privatization in the public sector. We
could also think metaphorically about this notion and recall the
extremely high levels of outward and circular migration that is often
cited as provoking anger among pauperized Bulgarians. Millions of
workers and their families have been pushed outside the country
precisely as a result of dying and dead industries and the assault on
the means of social reproduction that we spoke about earlier. Migration
has become the necessary way out of this social quagmire and it is the
means by which Bulgarians struggle with the gap created by the
impossibility to find dignified jobs, on the one hand, and the erasure
of more and more means to ensure the social security previously
guaranteed by the socialist system on the other. Perhaps
we could end by saying that unfortunately, the protests are still small
and relatively disorganized. Yet, one thing that is often hidden from
sight both in Bulgarian and Western media is that protests take place
almost on a daily basis in Bulgaria. Just in the past month we witnessed
demonstrations that tackled various issues: the social war declared on
people with disabilities; the miners falling victim to the contradiction
between the privatization of public domains and the ecological
question; the violence against women; the inadequate and offensively
small pensions, to name just a few. People in Bulgaria are on the
streets and fighting.
Hannah Schultes is an editor of the monthly newspaper ak - analyse und kritik and lives in Berlin.
Neda Genova is a PhD candidate in Cultural Studies at Goldsmiths College University of London and a co-editor of dversia.net, a Bulgarian magazine for left political critique.
Raia Apostolova is a sociologist.
Zhivka Valiavicharska teaches political and social theory at Pratt Institute, New York, and currently divides her time between New York, Sofia, and Plovdiv.